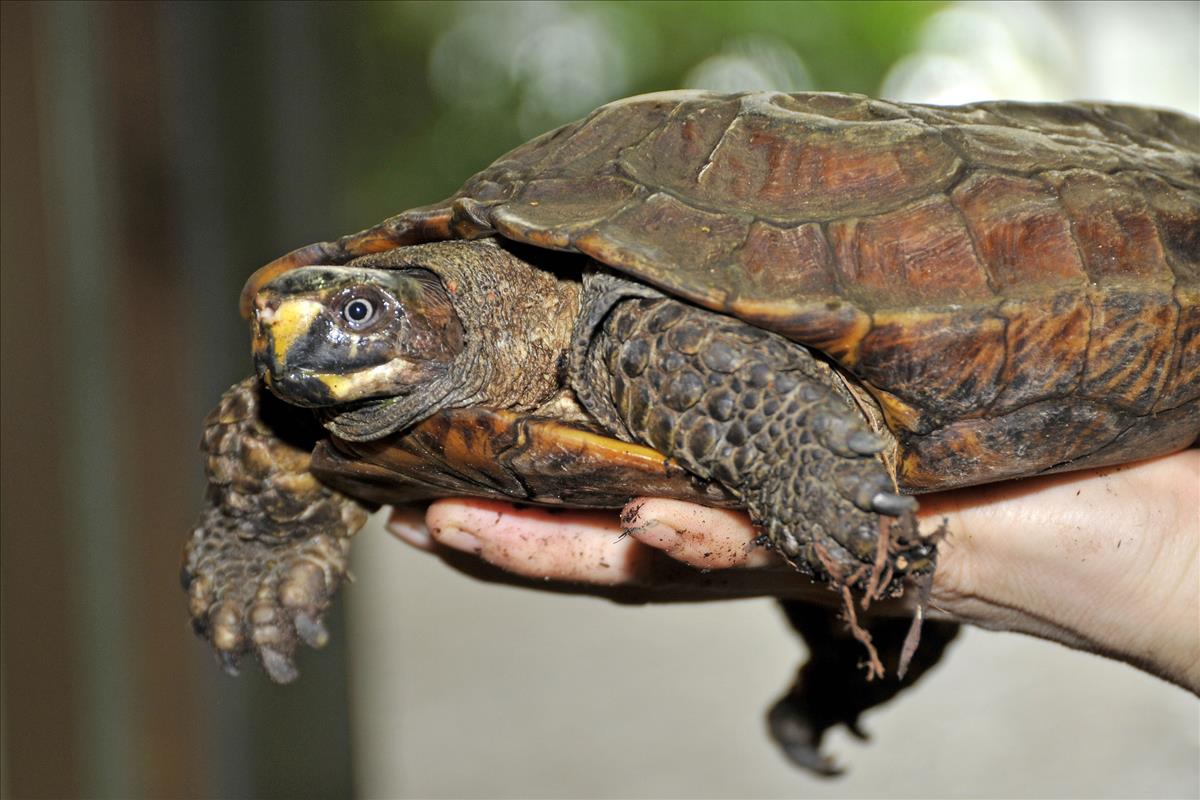
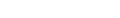Spiny turtle
Heosemys spinosa
The carapace of this unique turtle is sharp and pointed with a spiny keel and spiky serrated edges. There are also smaller spines on the pleural scutes, creating the effect of a walking pin cushion. This characteristic is especially noticeable in young turtles. The serrated carapace edge and spiny keel become worn down and are lost with age. Large adults have spineless carapaces and are much smoother than juveniles. The carapace is brown with a pale streak down the central keel, and the head and limbs are grayish-brown, usually with a yellow to red spot behind the eye and similar coloured speckling on the legs. The plastron is buff coloured with an intricate pattern of dark radiating lines on each scute. Males have longer, thicker tails than females and have concave plastrons.
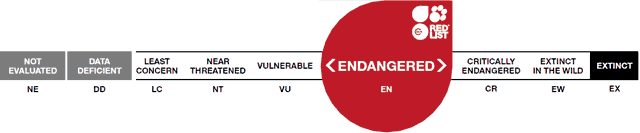
Conservation Status: IUCN
Distribution
The spiny turtle is found throughout peninsular Thailand and the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra, Borneo, and various small Indonesian Islands.
Habitat
These “freshwater” turtles live in or near shallow rainforest streams in wooded and forested hill and mountain regions where they frequently wander about on land in cool, humid, shaded areas.
Diet
These turtles in the wild are primarily herbivorous and somewhat frugivorous. They feed on a variety of vegetation and fallen fruit. They may also feed on invertebrates and carrion and in our zoo they will also eat meat.
Reproduction
Mating behavior is apparently stimulated by rains, with males becoming excited when sprayed with water in captivity, chasing females in an attempt to mount. Females lay two to three large eggs a season, usually at night or in the early morning. To enable the passage of these relatively large eggs, a hinge develops in the female’s plastron to allow greater flexibility during egg-laying. There have only been a handful of successful captive breeding efforts and those that have been successful have had incubation periods of 106 days, 110 days and 145 days. The period of incubation depends to some extent on temperature. Like all species of turtles, there is no parental care given to the offspring.
Adaptation
It is semi-aquatic but they often hide under plant debris or clumps of grass. Cryptic colouration helps camouflage the turtle amongst the leaf litter of its forest habitat. Young may be more terrestrial than adults. The spiny “armour” acts as a deterrent to predators, such as snakes.
Threats to Survival
These turtles are hunted by collectors for their unusual appearance and pattern. They are also hunted for the Asian food market and international pet trade. Destruction of its habitat also contributes to numbers rapidly declining in the wild. It is very difficult to breed in captivity. Only a handful of institutions have been successful, the Toronto Zoo being one of them.